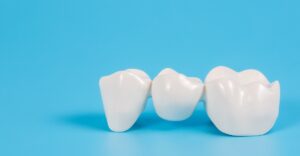
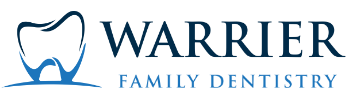A dental bridge is an appliance used to replace one or more missing teeth. These appliances are cemented into place and are not removable by the patient.
A bridge is made out of three parts that are used to replace the missing teeth: a pontic tooth (or false tooth), held together by two crowns(a "cap" that covers the adjoining tooth, approximating its normal size and shape). This three(or more)-piece appliance is then cemented to the abutment teeth (the teeth adjacent to the gap where teeth are missing).
Ideal Candidates for Dental bridge
Nearly everyone who has one or more missing teeth is a candidate for a dental bridge. However, several factors affect the success and longevity of the dental bridge. Some of these are the presence of existing gum disease and its extent, any shifting of teeth that might have occured of adjacent and opposing teeth and very importantly, the level of oral hygiene maintained.
Types of Dental bridges
There are several different types of dental bridges. Your dentist will recommend the most suitable one for you, based on the number and position of missing teeth.
Traditional bridge – a pontic tooth (or false tooth) is held together by two crowns (a "cap" that covers the tooth, approximating its normal size and shape)and cemented to the abutment teeth (the teeth adjoining the missing teeth).
Resin bonded bridge (also called "Maryland" bridge) – in this type of bridge, the pontic (false) tooth is held in place by wing-like metal extensions and bonded to the back of the abutment teeth with a resin cement. This type of procedure is applied more often when the teeth missing are in the front of the mouth. These types of bridges are considered to be more conservative of tooth structure but have a greater chance of debonding.
Cantilever bridge – this type of procedure is most appropriate when there are abutment teeth on one side of the missing tooth and no teeth on the other side.
Dental Bridges and Oral Health Care
The following are standard recommendations for all people but more so for patients with crowns and bridges in their mouth:
- Always brush your teeth after every meal with toothpaste and a soft toothbrush, as food may become lodged especially around the bridge causing the gums and teeth to become inflamed. This may lead to complications such as bone loss, resulting in the eventual loss of the bridge.
- Floss twice a day. Your dentist or hygienist may recommend using a floss threader or a product like Superfloss to get underneath the bridge for optimum cleaning in hard-to-reach areas.
- Schedule regular hygiene visits as recommended by your dentist.
- Limit your sugar and starch intake, especially snacking between meals, as debris left behind from these types of foods are converted into damaging acids which promote plaque formation.
- Avoid sticky snacks. This includes foods such as popcorn, hard or chew candy, caramel, and/or nuts. Try to munch on healthy snacks such as baby carrots, apples etc. Always brush after a snack.
Dental Bridge Durability
Most bridges last upto 8 to 10 years with proper oral care and hygiene maintenance.